The London Gardens of Sin and Sex
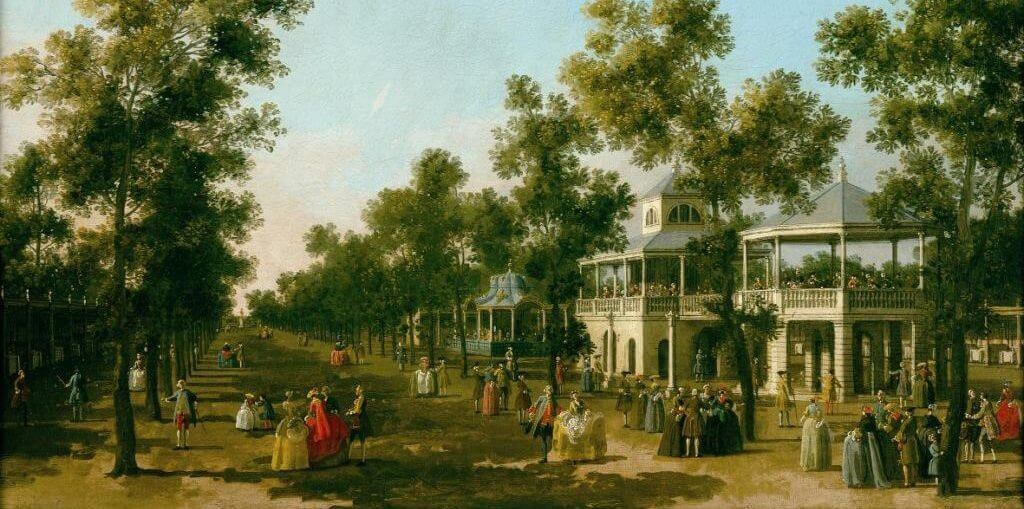

Pleasure rules at Vauxhall
Part II
source:bbc
af
Amsterdam, 18 May 2021–Music was a major draw for the 1,000 or so nightly visitors to Vauxhall, which hosted the leading musicians and composers of the day; George Frederic Handel made regular appearances; and Thomas Arne – best known for “Rule, Britannia!” – was Tyers’ in-house composer. There were fancy dress and masquerade balls, as well as raucous celebrations to mark major events. Paintings, sculptures, statues and other artworks were prominently displayed, while waiters served alcoholic drinks, cold meats, salads and cakes to diners seated in “supper boxes”.
The pleasure garden was the place where Londoners confronted their very best, and very worst, selves

Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens was once the greatest entertainment venue in London
Vauxhall appealed to all the senses,” said Coke.
“The streets of London at the time were smelly, dangerous, noisy, but you went to Vauxhall and could relax, feel free, a world apart. It became like an addictive drug.”
That’s why The presence of celebrities and royalty – such Frederick Louis, Prince of Wales, who was the landlord of the site – helped to attract the crowds, but Tyers had an egalitarian outlook and a desire to provide something of a cultural education.
Vauxhall was open to all members of society: for many years the admission fee was a shilling (roughly £15-20 today), which made the pleasure gardens accessible to a diverse audience.
There was also a greater degree of mixing between the sexes, enabling people to push at the restrictions of Georgian life. Needless to say, sex was a key element of Vauxhall, which had plenty of secluded areas suitable for romantic encounters, as well as sex work.
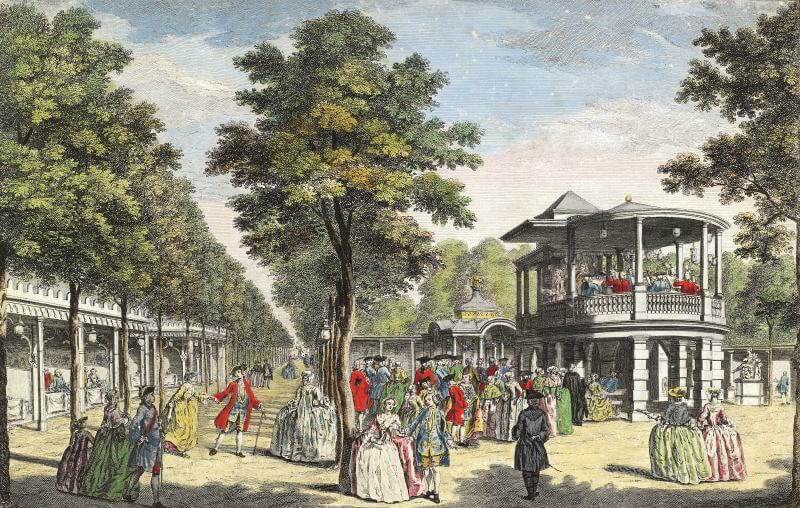

“It was one of the few places where the classes and sexes could mix freely,” said author Laura Shepherd-Robinson, whose new book, Daughters of Night, opens with the discovery of a murdered woman in Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens. “There was a glamorous, fashionable side – the finest in society turned out in their best clothes and were written about by journalists – but also definitely a tackiness.
And then there was the sleazy bit. It was a venue for scandalous liaisons and secretive assignations. Mothers were warned to take great care of their daughters and not to let them out of their sight as they could be seduced by a handsome butcher or whatever.”
The architecture, design and art of the pleasure gardens also brought the world – or at least a certain Georgian and early Victorian perspective of the world – to many people who would never have the opportunity to travel. There were Italian-style piazzas, representations of the ancient ruins of Palmyra in what is now Syria, and Chinese-influenced pavilions. “Going to Vauxhall was like going to another country, said Coke. “You could see little bits of foreign lands without leaving London.”

Vauxhall spawned many imitators. At one stage London had more than 60 pleasure gardens, and there were others across Britain and in continental Europe, the US, Russia and Australia. Yet as the 1800s progressed, Vauxhall struggled to keep up with the changing tastes of its audience. The wealthy, fashionable set drifted away, and the introduction of firework displays, ballooning, tightrope walkers and other spectacles provided only a temporary fillip. The management changed hands several times but always lacked Tyers’ magic touch. New forms of entertainment – notably music halls and seaside piers – became increasingly popular, while the growth of the railways allowed people to spend their leisure time further afield.
Moreover, as the capital expanded, outlying areas like Vauxhall were swallowed up. Land values increased until eventually it became more profitable to redevelop the site than maintain the pleasure gardens. On 25 July 1859, Vauxhall closed its doors for good. Three hundred homes were subsequently built, many of which were damaged or destroyed 80 years later in the Blitz, before slum clearances in the 1960s and ’70s largely completed the job. In 1976 a park named Spring Gardens was built on the site.
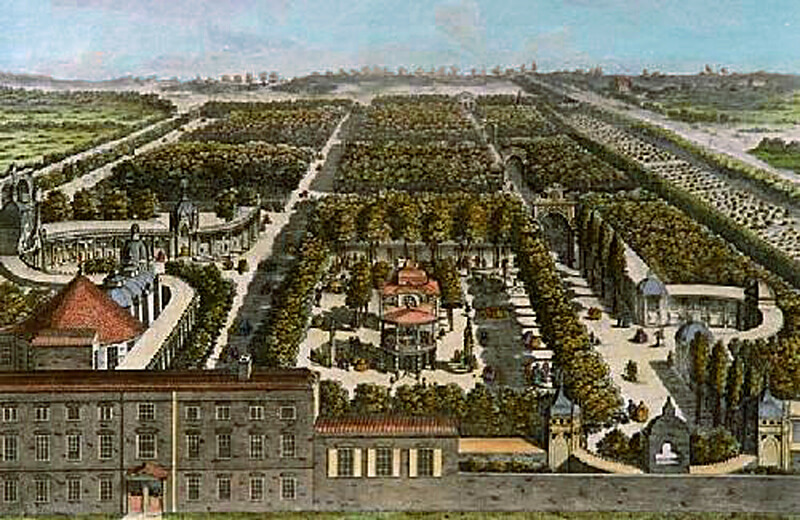
The past decade has seen renewed interest in Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens, with exhibitions at the Museum of London and the Foundling Museum, and appearances in the 2018 TV adaption of Vanity Fair and Netflix’s Bridgerton. In 2012, Spring Gardens was revamped and renamed Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens. Information boards now provide an overview of the history, and a striking pair of modern 18m-high concrete columns topped with sculptures – a modern man offering a flower to an 18th-Century woman; a nod to the park’s past and current incarnations – stand at the main entrance. The excesses of the pleasure gardens, though, are not encouraged, with signs warning visitors they are in a “controlled drinking zone”.
And drinking they did, as they sang their songs and danced their dances.
af
source: bbc