The London Open Gardens for Pleasure and Sin
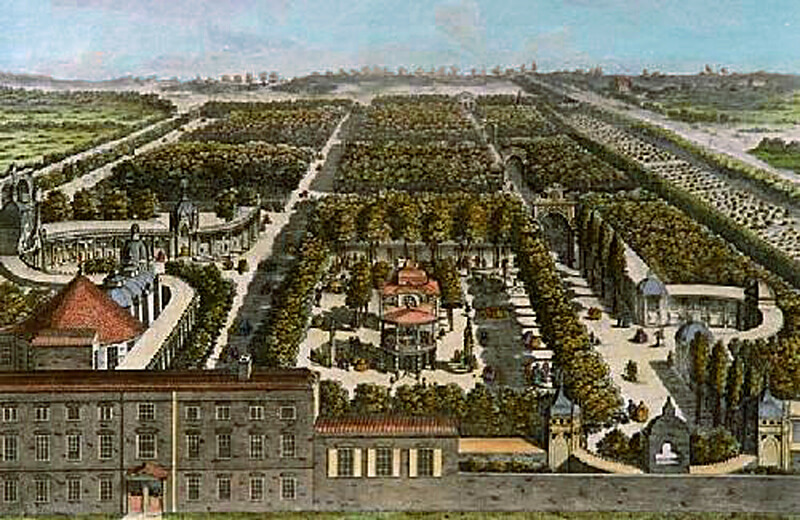
The Vauxhall Gardens
from the bbc
Amsterdam, 18 May 2021– A flash of green amid traffic-choked roads, elevated railway lines and anonymous high-rise apartment and office blocks, Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens is a well-kept but unremarkable south London park.
When I visited on a sunny spring afternoon, wildflowers dotted the grass and shouts sounded from the football pitch. At the edge of the seven-acre park, mesmerised children gazed at a trio of freshly trimmed alpacas, residents of Vauxhall City Farm. In the distance loomed the headquarters of the Secret Intelligence Service, an ironically distinctive green-and-cream hulk on the south bank of the Thames.

It may not look it now, but this area was once home to the greatest entertainment venue in Georgian London. The original Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens was a centre of culture, spectacle, intrigue and scandal during the 18th and 19th Centuries, immortalised in paintings by artists such as Canaletto and William Hogarth and in novels like William Thackeray’s Vanity Fair, which noted that “there is no headache in the world like that caused by Vauxhall punch”. Frequented by everyone from Charles Dickens to Venetian playboy Giacomo Casanova, Vauxhall transformed the capital’s nightlife and helped Londoners shake off some of the shackles of everyday life.
“It was a place where the glittering world of wealth, fashion and high culture showed off its seedy underside; where princes partied with prostitutes, and the middle classes went to be shocked and titillated by the excess on display,” wrote curator Danielle Thom in a series of articles on pleasure gardens for the Museum of London. “Simultaneously an art gallery, a restaurant, a brothel, a concert hall and a park, the pleasure garden was the place where Londoners confronted their very best, and very worst, selves.”

Emerging in the early decades of the 1700s on what was then the rural outskirts of London, pleasure gardens were enclosed outdoor spaces where people paid an admission fee to spend a summer evening eating, drinking, checking out the latest cultural offerings, and – in many cases – indulging in some rather more risqué and insalubrious activities. There were pleasure gardens in Chelsea and Marylebone, among other places, but the most famous and influential was Vauxhall.
The 12-acre site was originally known as New Spring Garden, which had been a place to drink, socialise and engage in illicit encounters since the 1660s. But it came into its own in 1729 after being sublet to an entrepreneur named Jonathan Tyers, who transformed the site into a fixture on the capital’s nightlife scene for more than a century. “It was where everybody wanted to go because it was where everyone else went,” said David Coke, co-author of Vauxhall Gardens: A History. “You went to Vauxhall to see what was happening, who was Under Tyers, Vauxhall encompassed landscaped gardens, woodlands, water features and tree-lined avenues.
There were pavilions, colonnades, porticoes, grottos, plazas and a rotunda, the architecture drawing on a patchwork of influences from Europe, the Middle East and Asia.
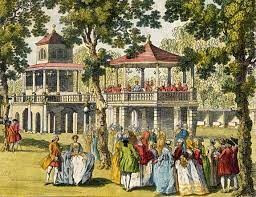
New features were added constantly and some elements broke new ground: a bandstand known as the Orchestra was “possibly the first building in London designed specifically and solely for the performance of music,” according to Coke.there, what people were wearing, what they were doing, who they were mixing with.
It was a huge source of gossip – the social media of its day.”
Although few material elements remain, the legacy of the original Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens lives on. Coke believes that it helped to lay the groundwork for London as a modern, cosmopolitan city and a cultural, culinary and nightlife capital, something highlighted by the presence of iconic LGBTQ+ venue the Royal Vauxhall Tavern, which was built in 1862, shortly after the pleasure gardens closed, and now sits at the edge of the park.
Going to Vauxhall was like going to another country.
The pleasure gardens didn’t finish, they just morphed into other things,” he said. “They are our television, films, cafes and foreign travel. Vauxhall’s DNA is everywhere.”
And perhaps, given the current circumstances, they are due a comeback. “There isn’t really any reason you couldn’t make them work today,” said Shepherd-Robinson. “Wouldn’t it be fabulous to have art exhibitions and dining under the stars? It would be great for the pandemic.”

After leaving the park I cut through an underpass to Vauxhall Station. The walls were covered with a mural of the pleasure gardens in their heyday, as well as an extract from an 18th-Century ballad that provided a final echo of the past:
“Each profession, ev’ry trade
Here enjoy refreshing shade,
Empty is the cobbler’s stall,
He’s gone with tinker to Vauxhall,
Here they drink, and there they cram,
Chicken, pasty, beef and ham
Women squeak and men drunk fall
Sweet enjoyment of Vauxhall.”
bbc